
Supporting the development of Geometrical Reasoning
RMFII Instructions
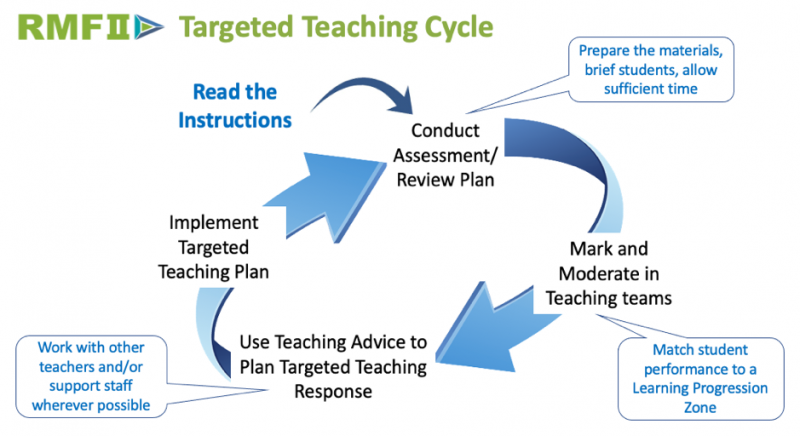
Before using the resources, please ensure that you read the instructions carefully.
The RMFII assessment forms should not be treated as ‘tests’. They contain important advice about:
- preparing the materials (i.e. booklets and any necessary resources (e.g. a paper folding activity for two of the Geometry Forms);
- briefing students to ensure they understand the purpose of the assessment and how their work will be assessed (a sample item is included for this purpose);
- supporting students; and
- timing – the assessments should be worked on for no more than about 33-35 minutes at a time – students need to be able to do as much as they possibly can for the results to be valid.
The RMFII Instructions can be found here.
Geometrical Reasoning Assessment Forms
There are four Assessment Booklets (Forms) for Geometrical Reasoning. These can be used to identify where learners are on the Learning Progression for Geometrical Reasoning and to evaluate learning over time (i.e. as pre and post intervention assessments).
In addition to the assessment items, each Form contains form-specific Scoring Rubrics, a Student Score sheet, and a Raw Score Translator. These do not need to be printed as they for teacher use only.
Print the Assessment Booklet on one side only and staple to keep student’s work together. Students can use the back of the previous page if additional working space is needed.
Marking student work in teaching teams has been found to be a particularly powerful form of professional learning, so teachers are encouraged to mark and moderate together wherever possible.
The RMFII Geometrical Reasoning Assessment Forms can be found here:
Geometrical Reasoning Learning Progression and Teaching Advice
The Geometrical Reasoning Learning Progression was derived from well over 3500 student responses to a range of rich tasks. Rasch analysis, which allows both students’ performance and item difficulty to be measured using the same unit and placed on an interval scale, was used to create an ordered scale for geometrical reasoning ranging from naïve and limited forms of reasoning (Zone 1) to sophisticated, abstract forms of geometrical reasoning (Zone 8).
Student performances are mapped to the scale where they have more than a 50% chance of scoring at the level required for the items located below that point on the scale but less than a 50% chance of scoring at the level required for items located above that point. This means that there are some aspects of the behaviours identified within the relevant Zone that need to be Consolidated and Established to deepen students’ understanding and others that need to be Introduced and Developed to progress their learning to the next Zone.
Note that what is Introduced and Developed in one Zone is Consolidated and Established in the next Zone.
Three big ideas underpin geometrical reasoning:
- Hierarchy and Properties
- Transformation of Relationships, and
- Geometric Measurement.
These big ideas are underpinned by three pillars: Visualisation, Language and Discourse, and Representations. These three pillars are intertwined and are integral to all teaching and learning in the area of Geometry.
The Geometrical Learning Progression and the associated Teaching Advice have been structured around these three big ideas and pillars.
Indicative activities and links to related teaching resources are included in the Teaching Advice.
A summary of the Geometrical Reasoning Learning Progression can be found here.
The Geometrical Reasoning Teaching Advice can be found here.
Professional development Modules
A suite of online modules has been prepared by members of the RMFII research team to support school-based professional development for multiplicative thinking and mathematical reasoning.
These are aimed at:
- deepening teacher knowledge and confidence for teaching multiplicative thinking and mathematical reasoning;
- exploring the learning progressions and related teaching advice for algebraic, geometrical, and statistical reasoning as well as multiplicative thinking; and
- considering a range of activities that can be used in mixed ability groups across different zones to maximise learning for all students.
The modules for geometrical reasoning are being finalised and will be added shortly.